As blockchain technology keeps changing industries from finance to supply chain, more and more businesses are looking for ways to bring it into their daily operations. But building a blockchain solution isn’t something that can be done easily, it needs the right mix of technical knowledge, long-term vision and real hands-on development skills, which many companies usually don’t have inside their team.
That’s exactly where blockchain development outsourcing comes in. Rather than building and maintaining an in-house team, companies can work with outside blockchain professionals who help to plan, develop and launch blockchain-based systems faster and more effectively.
In this guide, we’ll go through all the key things you should know about blockchain outsourcing such as what it really means, why it’s useful, some risks that might come up and how you can pick the right development company for your project.
Why Are Governments Turning to Blockchain?
Governments face lots of challenges in public services like slow processes, outdated systems and the ever –present risk of fraud. Blockchain is helping tackle these problems while bringing several useful benefits :
- Stronger Security: Blockchain uses cryptographic encryption and decentralization to make data pretty much impossible to tamper with or hack, helping protect sensitive government info like voter records and financial transactions. This also kind of reduces the risk of cyber attacks and fraud.
- Transparency: Blockchain’s immutable ledger records government activities permanently and mostly publicly, letting people track budgets, procurement and policies in real-time which helps build public trust and accountability.
- Efficiency: By automating workflows with smart contracts and cutting down on paperwork and middlemen, blockchain speeds up government processes, lowers costs and reduces corruption across services like land registries and procurement.
- Fraud Reduction: Transactions on a blockchain are mostly permanent and verifiable which reduces the chance of fraud or manipulation happening. This makes both financial and administrative processes more reliable.
- Better Citizen Services: With accurate, secure and faster systems, citizens get services they can depend on. Governments can also respond to requests or issues more efficiently and effectively.
The Benefits of Using Blockchain in Government & Public Sector?
Blockchain brings numerous benefits to various areas of government and public administration, making processes more secure, transparent and efficient. Here’s how it creates impact:
- Enhanced Security and Data Integrity: Blockchain stores data across lots of computers, so it’s really hard for anyone to hack or change it without being noticed. This helps governments keep sensitive information safe and makes sure records mostly stay correct over time.
- Increased Transparency and Trust: Every action on a blockchain can be checked which means people can see how government decisions are made. This builds trust because people can kind of check things themselves instead of just taking someone’s word for it.
- Streamlined and Automated Processes: Smart contracts can automatically do tasks once certain conditions are met which reduces paperwork and waiting time. Government employees can spend more time on actual work instead of constantly checking forms and approvals by hand.
- Reduction in Fraud and Corruption: Because blockchain records can’t really be changed secretly, it’s a lot harder for anyone to cheat the system or pull off fraud. Procurement, taxes and benefits become more traceable which makes corruption less likely to happen.
- Improved Citizen Services via Digital Identity: Blockchain lets citizens manage their own digital ID, so they don’t need to carry papers or repeat verification over and over again. This makes accessing services faster, safer and more convenient for pretty much everyone.
Use Cases of Blockchain in Government
Blockchain isn’t just some theory anymore; it’s already being used in several government areas. Here are a few key places where blockchain is actually making a real impact:
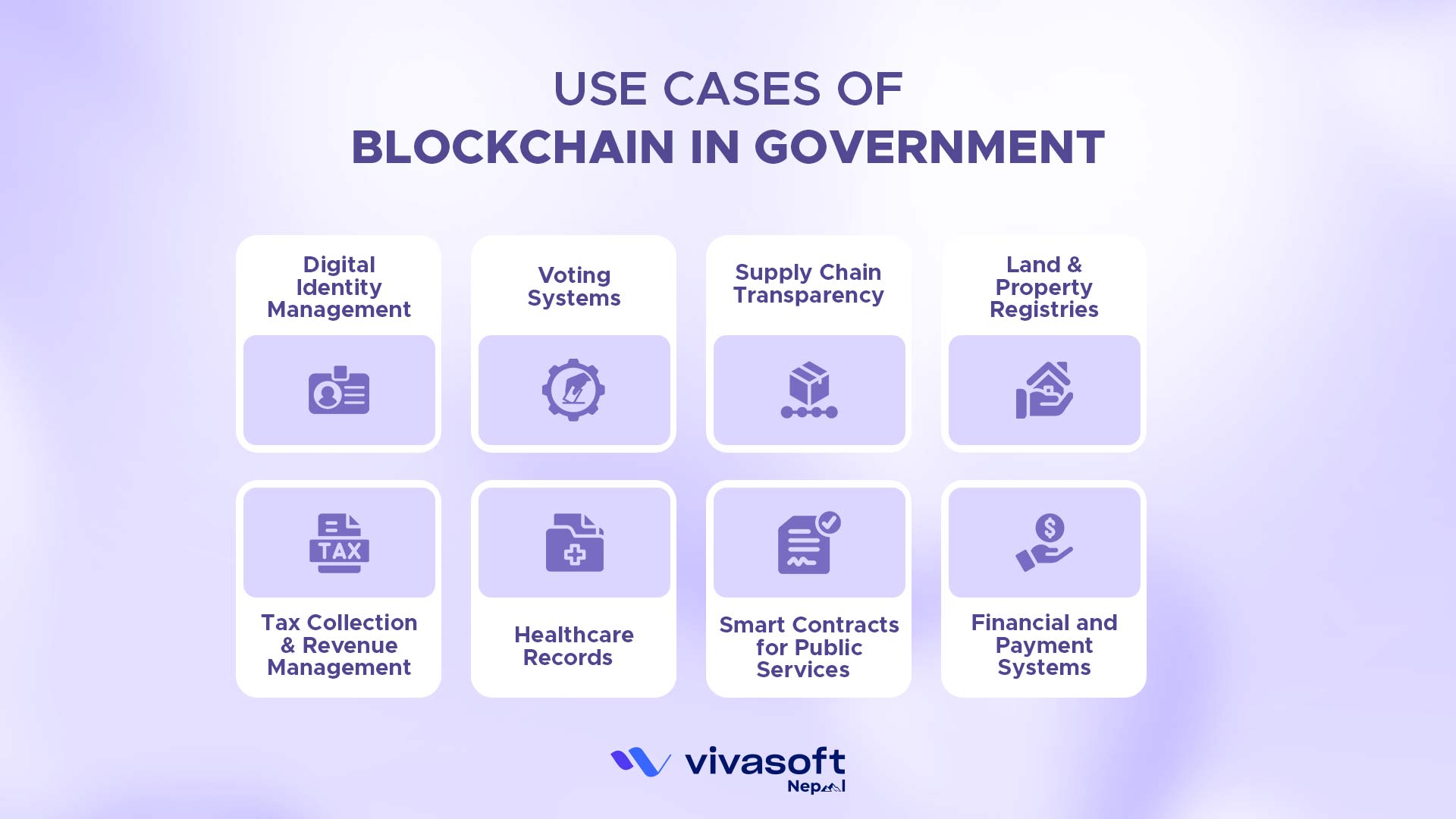
1. Digital Identity Management
Blockchain enables citizens to have secure, verifiable digital identities that they control. This helps reduce identity fraud and lets people get government services without having to submit physical documents again and again.
Estonia is probably the most well-known example, with its e-Residency program letting residents and businesses access government stuff online, like paying taxes and signing documents legally; all without ever going to an office.
2. Voting Systems
Blockchain can make elections more secure, transparent and convenient. It makes sure votes are recorded correctly and gives verifiable audit trails without really compromising voter privacy.
For example, West Virginia in the US tried out blockchain-based voting for overseas military personnel, letting them cast votes safely from anywhere. Moscow has also tested blockchain voting for local elections, making sure votes are counted properly and can’t really be tampered with.
3. Supply Chain Transparency
Blockchain helps governments keep track of goods in complex procurement and supply networks making things more efficient and helping prevent fraud or counterfeiting.
For example, the U.S. FDA has used it to track pharmaceuticals from manufacturers to pharmacies, stopping counterfeit drugs. Humanitarian organizations also use blockchain to make sure aid supplies actually reach the people who really need them.
4. Land & Property Registries
Blockchain can help secure property ownership records, reduce disputes and speed up transactions. It gives an immutable record that’s more or less transparent and trustworthy.
For example, Ghana has implemented blockchain land registry to minimize disputes. Georgia uses blockchain to maintain transparent property records while Sweden piloted blockchain for land registration, cutting transaction times from months to just a few days.
5. Tax Collection & Revenue Management
Blockchain improves tax collection transparency, reduces fraud and can automate calculations for efficiency. Governments can track economic activity more accurately using this technology.
For example, China issues billions of blockchain-based invoices to monitor business transactions making audits easier. Smart contracts can also automatically calculate and collect taxes on certain transactions.
6. Healthcare Records
Blockchain secures patient data while allowing authorized sharing between healthcare providers. It also gives patients more control over who accesses their information.
For example, Estonia’s healthcare system uses blockchain to manage medical records securely. Hospitals and clinics can access patient data efficiently while patients control visibility to protect privacy and reduce errors.
7. Smart Contracts for Public Services
Smart contracts automate government processes, cutting down on bureaucracy and human errors. They basically make sure rules get executed automatically once the conditions are met.
For example, Dubai plans to execute all government transactions via blockchain using smart contracts to automatically issue permits, distribute grants and process social benefits.
8. Financial and Payment Systems
Blockchain enables faster, cheaper and more transparent payments. It can streamline cross -border transfers and government disbursements, making sure funds actually reach the right recipients.
For example, Central Bank Digital Currencies like China’s digital yuan, the Bahamas’ Sand Dollar and the Eastern Caribbean’s DCash are some of the early examples. Blockchain also helps governments distribute pensions and benefits more securely without delays or much chance of fraud.
What Are the Challenges of Implementing Blockchain in Government?
While blockchain sounds pretty promising, getting it into actual government systems isn’t really that simple. There are still a few real-world challenges that make adoption bit tricky.
- High Initial Costs and Infrastructure Requirements: Setting up a blockchain system can be expensive at first since it needs proper hardware, software and maintenance. For many government offices that kind of upfront investment can feel a bit too heavy to manage right away.
- Regulatory and Legal Considerations: Rules and laws around blockchain are still kind of unclear in most countries. Governments have to make sure their systems meet legal standards before using it widely which can take a lot of time and back-and-forth.
- Technical Expertise and Training: Not every government department has people who fully understand how blockchain works. So, extra training and hiring skilled professionals become necessary which adds another layer of challenge.
- Scalability and Interoperability Concerns: As blockchain networks grow, handling large amounts of data smoothly can get tricky. Plus, getting different systems or departments to work together on the same platform isn’t always that easy.
Conclusion
Blockchain is slowly but surely changing how governments operate making systems more transparent, secure and efficient. From digital IDs and land records to healthcare and voting; it shows how public data can be managed safely and effectively. Still, many governments are just getting started with it. The adoption takes time, planning and the right people behind it but the results can be worth it.
If your organization is considering about getting started, now’s probably the right time to look into it. You can outsource blockchain development company that specialize in helping governments and public sectors implement these solutions the right way.
FAQs
Who actually uses bockchain?
Blockchain is used by a mix of people and organizations from banks and tech companies to government departments. It’s basically for anyone who needs secure and transparent data handling.
Is blockchain monitored by the government?
Not exactly. Governments can set some rules around how it’s used but blockchain itself runs on decentralized systems so there is really no single body that fully controls it.
Which type of blockchain concentrates on the government sector?
Private or permissioned blockchains are used since they offer more control and privacy. Some governments also test hybrid models for specific use cases.
Which country uses blockchain in government?
Several countries like Estonia, Georgia, Sweden and Dubai have already put blockchain to use for digital identity, land registries and e-governance services.













