Finance is changing fast. DeFi short for decentralized finance isn’t just a buzzword anymore. By 2026, it’s part of how people lend, borrow, trade and even stake money. Decentralized finance is taking off because it removes the middlemen like banks and let people interact directly through smart contracts. This shift isn’t just technical, it is changing the way we think about money and trust.
This makes DeFi smart contract development a key focus for the developers and businesses alike. These contracts handle complex financial logic, ensure trustless operations and automate transactions in a ways traditional systems can’t. Getting them right is critical because even small errors can have a major financial consequences, making smart, secure and efficient DeFi contract development more important than ever.
What is DeFi Smart Contract Development?
At its core, a smart contract is just code that runs on blockchain and execute automatically when conditions are met. But in DeFi, these contracts are far more than simple token transfers, they handle lending, staking, automated trading and more. A DeFi smart contract is designed specifically to interact with financial protocols, often connecting with other contracts to form complex systems of money flow.
Unlike traditional blockchain smart contracts which can be simple “if-this-then-that” scripts; DeFi contracts are highly composable. They’ve evolved from single-purpose contracts for basic tokens to multi-layered systems managing interest rates, liquidity pools, synthetic assets and algorithmic governance. This evolution has unlocked new possibilities for financial innovation but also new challenges in coding, testing and security.
What Are the Process for DeFi Smart Contract Development?
Developing DeFi smart contracts usually follows a step by step process. Each stage builds on the previous one to minimize financial risk, security issues and design mistakes before real assets go on-chain.
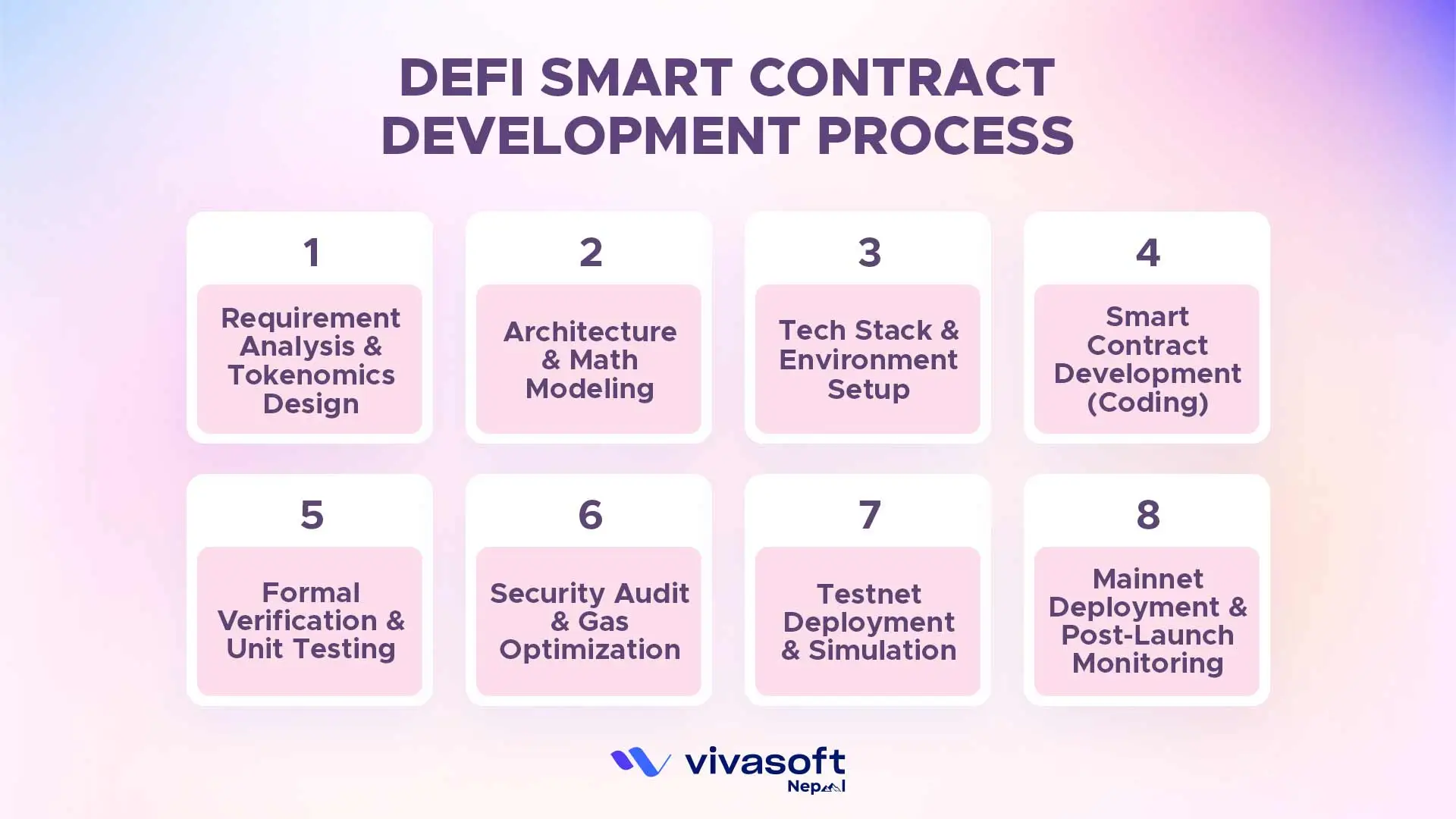
Step 1: Requirement Analysis & Tokenomics Design
The first step is figuring out what the DeFi protocol is actually meant to do. This includes defining financial model like how tokens are minted, burned or distributed, and how fees or rewards will work. Tokenomics is super important because even a perfectly coded contract can fail if the economics are off. Teams also decide whether to fork an existing protocol or build everything custom; depending on flexibility, security and long-term goals.
Step 2: Architecture & Math Modeling
Once the requirements are clear; the team designs the overall architecture and how contracts will interact with each other. A big part of this step is math modeling like calculating APR, APY, bonding curves and liquidation formulas. Even a small errors here can cause big losses; so this phase usually takes multiple reviews and careful planning.
Step 3: Tech Stack & Environment Setup
Once the design is done, developers get the coding environment ready using tools like Hardhat, Foundry or Truffle. They also choose which blockchain the contracts will run on like Ethereum, Polygon or Layer-2 networks to save on gas fees. Having the right setup and a tools makes testing, debugging and later deployment a lot easier and less stressful.
Step 4: Smart Contract Development
Now comes the coding part. Developers write the contracts using Solidity or Vyper to handle swaps, lending, staking, rewards or whatever the protocol needs. They also implement standard interfaces like ERC-20, ERC-721 or ERC-4626 to make sure the contracts work with wallets, dApps and other DeFi protocols.
Step 5: Formal Verification & Unit Testing
Before anything goes live, contracts are tested carefully in local environments. Developers write unit tests aiming for near 100% coverage and check for common problems like reentrancy or logic errors. Catching issues here saves a lot of trouble once the contracts are on mainnet.
Step 6: Security Audit & Gas Optimization
Security audits are a must in DeFi. Tools like Slither scan the code first, then third-party firms perform detailed audits to find vulnerabilities. At the same time, developers optimize gas usage to keep transaction costs low and after audits; the code is usually frozen to prevent last-minute changes.
Step 7: Testnet Deployment & Simulation
Before launching on mainnet; contracts are deployed to testnets to see how they perform in real-world conditions. Many teams also fork the mainnet with tools like Tenderly to simulate actual usage. Some projects even invite the community for beta testing or bug bounties to catch any edge cases that internal teams might have missed.
Step 8: Mainnet Deployment & Post-Launch Monitoring
Finally, the contracts are deployed to the mainnet with proper safety measures in place. Admin keys are usually protected with multi-sig wallets so there is no single point of failure. After launch , developers keep monitoring the contracts using tools like The Graph and stay ready to pause or react fast if anything unexpected pops up.
How Does DeFi Smart Contracts Work?
DeFi smart contracts operate as autonomous programs on the blockchain, executing predefined logic without a human intervention. Once deployed; they respond to transactions based on their code.
On-Chain Execution Logic
In DeFi, all the important financial logic happens directly on-chain. Things like updating user balances, calculating interest, triggering liquidations or distributing rewards are handled automatically by the smart contracts. Since everything is executed on the blockchain; the process is transparent and anyone can verify what happened by checking the transaction data.
Interaction Between Users, Wallets & dApps
Users don’t interact with smart contracts directly in a technical sense. Instead, they use wallets like MetaMask or mobile crypto wallets connected to decentralized applications (dApps). The dApp acts as a user-friendly layer but behind the scenes, every action still goes straight to the smart contract where the actual rules and logic are enforced.
Role of Oracles in DeFi Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are isolated from the outside world which means they can’t fetch real-world data on their own. This is where oracles come in. Oracles supply price feeds, market data and other external information that DeFi protocols depend on. If oracle data is inaccurate or manipulated, it can cause serious issues which is why reliable oracle systems are so important in DeFi.
Supported Blockchain Networks
Most DeFi smart contracts are built on Ethereum or Ethereum-compatible networks mainly because of their strong ecosystem and tooling. However, many projects now use Layer-2 solutions or alternative blockchains to reduce fees and improve speed. The choice of network directly affect performance, transaction costs and even security assumptions for the protocol.
The Key Components of DeFi Development
A DeFi ecosystem isn’t built from a single smart contract. It usually consists of multiple components working together each components are responsible for a specific financial task. When combined, these pieces create fully decentralized financial systems that can replace or improve traditional finance workflows.
DEXs & AMMs
Decentralized exchanges or DEXs, use Automated Market Makers (AMMs) instead of the usual order books. Instead of matching buyers and sellers AMMs let people trade directly against a liquidity pool. Protocols like Uniswap made this super popular because it works smoothly without needing a middleman.
People who provide liquidity add their tokens to these pools and get LP tokens in return. These tokens show their share in the pool and let them earn a part of the trading fees. Basically, the busier the pool, the bigger the rewards can be.
Decentralized Lending & Borrowing Protocols
Lending and borrowing protocols are designed to work without banks. To reduce risk, most of them use over-collateralization; meaning borrowers must lock up assets worth more than what they borrow. This helps protect lenders if market prices move suddenly.
If the value of collateral drops too much, liquidation mechanisms automatically step in. Flash loans take it further by letting users borrow money without collateral; as long as they pay it back in the same transaction.
Yield Farming, Staking, and Aggregators
Yield farming and staking smart contracts reward users for locking up their assets in a protocol. Rewards are distributed automatically based on predefined logic, removing the need for manual calculations or approvals.
Aggregators improve this process by automatically moving funds between protocols to maximize returns. They often auto-compound rewards which saves users time and reduces the need for constant interaction.
Tokenomics & Governance Tokens
Governance tokens let users have a voice in how DeFi protocol changes and grows. Token holders can vote on upgrades, fee structures and other important decisions; forming the foundation of decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs).
Vesting schedules and token distribution contracts are really important too. They stop large amounts of tokens from hitting the market all at once and make sure the supply is more predictable over time.
NFT Integration in DeFi (Fi-NFTs)
NFTs are no longer just collectibles in DeFi. Many protocols now treat them as financial assets that can be used within smart contracts. Some platforms allow users to lock NFTs as collateral in exchange for loans.
This approach opens up new liquidity models where users can access capital without selling their NFTs keeping ownership while still unlocking value from their digital assets.
What Advanced Features Do DeFi Smart Contracts Offer?
Modern DeFi smart contracts are no longer just limited to simple swaps or basic lending features. As the ecosystem matures these contracts now support more advanced financial logic and a cross-platform interactions.
- Cross-Chain Interoperability & Layer-2 Scaling: DeFi smart contracts can now interact across the different blockchains using bridges and cross-chain messaging protocols. This help improve liquidity flow while also reducing congestion and high fees through Layer-2 networks.
- Flash Loans & Institutional DeFi Logic: Flash loans enable users to borrow large amounts of capital without collateral; as long as the loan is repaid within a single transaction. This feature is often used for arbitrage, refinancing and other advanced strategies that appeal to institutional users.
- Account Abstraction Integration: Account abstraction makes smart accounts more flexible than traditional wallets. It allows features like gasless transactions and custom authorization rules which improves the overall user experience.
- Real-World Assets (RWA) & Synthetic Assets: DeFi smart contracts are increasingly used to tokenize real-world assets such as real estate, commodities or invoices. They also power synthetic assets that give user exposure to stocks or currencies without directly owning them.
- Advanced Liquidity Mechanisms: Modern liquidity models allow providers to concentrate their capital within specific price ranges instead of spreading it evenly. Combined with dynamic fee structures this helps improve capital efficiency and potential returns.
- Contract Upgradeability Patterns: Upgradeability patterns like proxy contracts allow protocols to update logic without redeploying everything from scratch. However, these systems require strong governance controls to avoid misuse or unexpected changes.
What Are the Benefits of DeFi Smart Contracts?
DeFi smart contracts bring new levels of efficiency, transparency and control to financial systems. They removes many traditional barriers by replacing intermediaries with code.

- Composability: DeFi protocols are designed to work together like a building blocks. This makes it easier for developers to create a new products by combining existing smart contracts.
- Complete Transparency & Immutability: All smart contract logic and transactions are recorded on the blockchain. Anyone can verify how the system works and once deployed, the rules can’t be secretly changed.
- Automation & Cost Efficiency: Smart contracts execute actions automatically without a manual approval or middlemen. This reduce operational costs and speeds up financial processes.
- Global Accessibility: DeFi platforms are open to anyone with an internet connection and a crypto wallet. Users don’t need bank accounts or geographic approval to participate.
- Self-Custody & Counterparty Risk Reduction: With DeFi smart contracts, users keep control of their assets in their own wallets. Since funds are not held by third parties; the risk of custodial failure or a counterparty issues is greatly reduced.
What Are the Common Challenges in DeFi Smart Contract Development?
Despite all the benefits, DeFi smart contract development isn’t straightforward. Building protocols that are both secure and scalable takes a lot of planning, testing and constant attention.
- High Development Complexity: DeFi smart contracts usually handle financial logic, security rules and user interactions all at once. If even one part isn’t designed properly; it can affect the entire protocol and lead to unexpected issues.
- Gas Optimization & Performance Issues: Poorly optimized code can result in higher gas fees; especially when network is busy. When transactions become expensive users may hesitate to interact with the protocol on a regular basis.
- Upgradeability & Maintenance Risks: Upgradeable contracts make it easier to fix bugs or add features later but they also raise trust and governance concerns. If upgrades aren’t handled carefully; they can reduce decentralization or open the door to new security risks.
- Reentrancy and Flash Loan Attacks: DeFi protocols are frequent targets for fast and sophisticated attacks. Small logic mistakes can be exploited in seconds through reentrancy or flash loan attacks if proper safeguards aren’t in place.
The DeFi Development Tech Stack (2026 Standards)
By 2026, DeFi development relies on more mature and standardized tech stack compared to the earlier years. These tools help teams build secure smart contracts, test complex financial logic and maintain scalable decentralized applications in production.
- Languages: Most DeFi smart contracts are written in Solidity , especially for Ethereum and other EVM-compatible blockchains. Some teams prefer Vyper because of its simpler syntax and reduced feature set while Rust is commonly used for a high-performance chains like Solana and parts of the Cosmos ecosystem.
- Frameworks: Hardhat is still widely used for flexible development, debugging and plugin support. Foundry has become something of a standard for modern DeFi projects, mainly because of its fast testing, fuzzing capabilities, and performance-focused workflow.
- Security Tools: Security tools are used throughout the development process, not just before launch. Slither, MythX, and Certora help identify vulnerabilities, unsafe patterns and logical errors early reducing the chances of serious issues during audits.
- Infrastructure: DeFi applications depend on reliable infrastructure to handle data and storage efficiently. The Graph is commonly used to index and query on-chain data while IPFS and Arweave provide decentralized storage for frontend assets and long-term data availability.
DeFi Smart Contract Examples by Use Case
Not all DeFi smart contracts do the same thing. Different protocols are built for different financial use cases, depending on what problem they are trying to solve. Below are some well-known examples that show how DeFi smart contracts are used in practice.
| Use Case | Example | Purpose / Function |
|---|---|---|
| DEX | Uniswap | Allows users to swap tokens using liquidity pools instead of order books |
| Lending | Aave | Lets users lend assets to earn interest or borrow by providing collateral |
| Yield farming | Compound | Helps users earn returns by supplying assets to the protocol |
| Governance | MakerDAO | Enables community governance and manages stablecoin issuance |
These examples show how smart contracts can handle everything from simple token swaps to complex governance decisions, all without relying on centralized control.
How to Hire the Right DeFi Smart Contract Development Team?
Choosing the right development team can make or break a DeFi project. Beyond technical skills, you also need to think about cost, timelines, and long-term reliability.
Cost and Timeline Estimation
The cost of DeFi smart contract development depends on how complex the protocol is, how many contracts are involved, and whether advanced features are required. Security audits usually take up a large part of the budget and can also affect the overall timeline.
In-House Team vs. Outsourcing Companies
Building an in-house team gives you more control and continuity, but it often comes with higher upfront costs and longer hiring time. Outsourcing companies can move faster and already have DeFi expertise, which is why many projects prefer to explore leading Defi development companies when getting started.
Legal & Compliance Considerations
DeFi regulations are different in every region and continue to evolve. A good team will include legal disclaimers, basic compliance checks, and an understanding of regulatory risks to avoid problems later on.
Conclusion
DeFi smart contract development in 2026 sits right at the intersection of finance, cryptography, and real-world software engineering. From designing tokenomics to running security audits, every step matters when you’re building decentralized systems that people actually trust and use.
If you’re planning to build a new DeFi product or enhance an existing one, working with experienced blockchain experts can help you avoid costly mistakes and build with confidence. From secure smart contract architecture to scalable DeFi solutions, the right team makes all the difference. If you’re looking to hire blockchain experts for DeFi smart contract development, choosing a team with proven experience can set your project up for long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the best language for DeFi smart contracts
Solidity is the most widely used for EVM-compatible blockchains, while Vyper and Rust are used for specialized cases on Ethereum and high-performance chains like Solana.
Can DeFi smart contracts be regulated?
The code itself isn’t regulated, but the teams, applications, and token offerings behind it may fall under financial regulations depending on the jurisdiction.
Do DeFi smart contracts require audits?
Yes. Audits are essential to detect vulnerabilities, logic errors, and security risks before deployment.
How much does a DeFi smart contract audit cost?
Costs vary depending on contract complexity, size, and number of features, often ranging from a few thousand to tens of thousands of dollars.
Can I modify a DeFi smart contract after deployment?
Only if upgradeable patterns were implemented from the start; otherwise, deployed contracts are immutable and cannot be changed.













