Blockchain technology has transformed how businesses store, share and secure data. Although public blockchains such as Bitcoin and Ethereum are accessible to anyone. However many companies are turning to private blockchains to enjoy the benefits of blockchain without compromising control, privacy or efficiency. Private blockchains offer a secure network. Only authorised participants can view data, perform transactions and validate blocks.
Unlike public blockchains, which are decentralized and accessible to anyone or consortium blockchains, which are semi-decentralized and controlled by multiple organizations. Private blockchains are fully controlled by a single organization or a group with centralized management. Some of the more widely used frameworks such as Hyperledger Fabric, Quorum and Corda are perfect for businesses seeking enterprise-level blockchain solutions.
In this guide, we’ll cover all you need to know about building a private blockchain. You’ll discover its main components and how to launch a fully functional network for your business.
What is Private Blockchain?
A private blockchain is the type of blockchain where only approved participants can join and access the network. It’s controlled by an organization or group, making it faster, more secure and suitable for business use. This makes them ideal for businesses that need confidentiality and compliance such as financial institutions , healthcare providers and supply chain networks.
Private blockchains offer key features like controlled governance, faster transaction speeds, customizable smart contracts and strong security. They are essential for businesses that handle sensitive data yet want to use the advantages of immutability and transparency of blockchain.
What Are the Components of Private Blockchain?
Private blockchains are like a team with each part playing a role. They keep the network secure and efficient. Here are the main components:
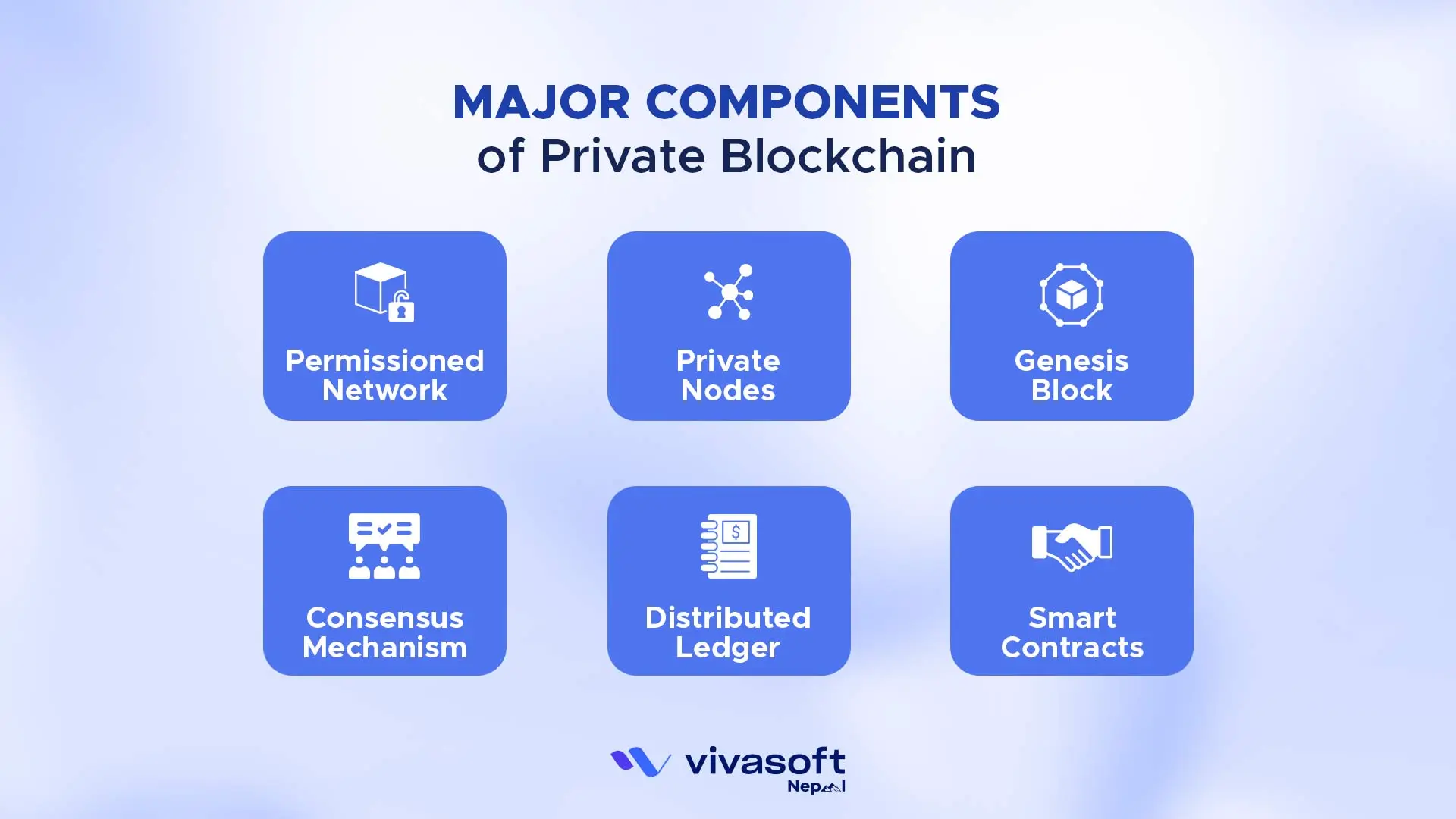
- Permissioned Network: Only authorized participants can access the blockchain ensuring security and controlled participation.
- Private Nodes: A select group of nodes maintains ledger copies and validates transactions. This helps keep the network both safe and efficient.
- Genesis Block: The first block. It starts the network and lays the foundation.
- Consensus Mechanism: Rules like RAFT, PBFT or PoA. They make sure all nodes agree on valid transactions.
- Distributed Ledger: Common record that keeps track of all transactions. Once written it cannot be changed. Only approved participants can access it.
- Smart Contracts: Code that runs itself. It enforces rules and handles tasks automatically on the blockchain.
These core components work together across different blockchain layers to ensure security, scalability, and modularity.
Private Blockchain for Business: A Features Checklist
Private blockchains are built specifically for business environments where privacy matters, transactions need to be quick and access can’t just be open to anyone on the internet. Here are some of the key features:
- Control Over Access: Only authorized participants can join and interact with the network.
- Centralized Governance: Policies and network rules are enforced by the organization or consortium governance.
- High Efficiency and Faster Transactions: Permissioned nodes and simple consensus like RAFT or PoA make transactions fast.
- Privacy and Confidentiality: Sensitive data is protected and shared only with approved parties.
- Smart Contract Automation: Chaincode or smart contracts handle business rules automatically.
- Integration and Customization: Connect blockchain easily to ERP, CRM or other systems using APIs or SDKs.
- Compliance and Data Governance: Follows regulations like GDPR and financial laws while keeping internal policies in check.
- Scalability: The network can easily add nodes or adjust consensus to handle growing transaction volumes.
- Cross-chain Interoperability: Use bridges or cross-chain connectors to interact with other blockchains.
- Security: TLS encryption, HSM/KMS key management and controlled access control lists (ACLs) protect data and transactions.
Step by Step Guide to Create Private Blockchain Platform
Private blockchains give businesses full control over their data, security and operations deciding who can participate and what actions they can take. Here’s a step by step guide to create a private blockchain:
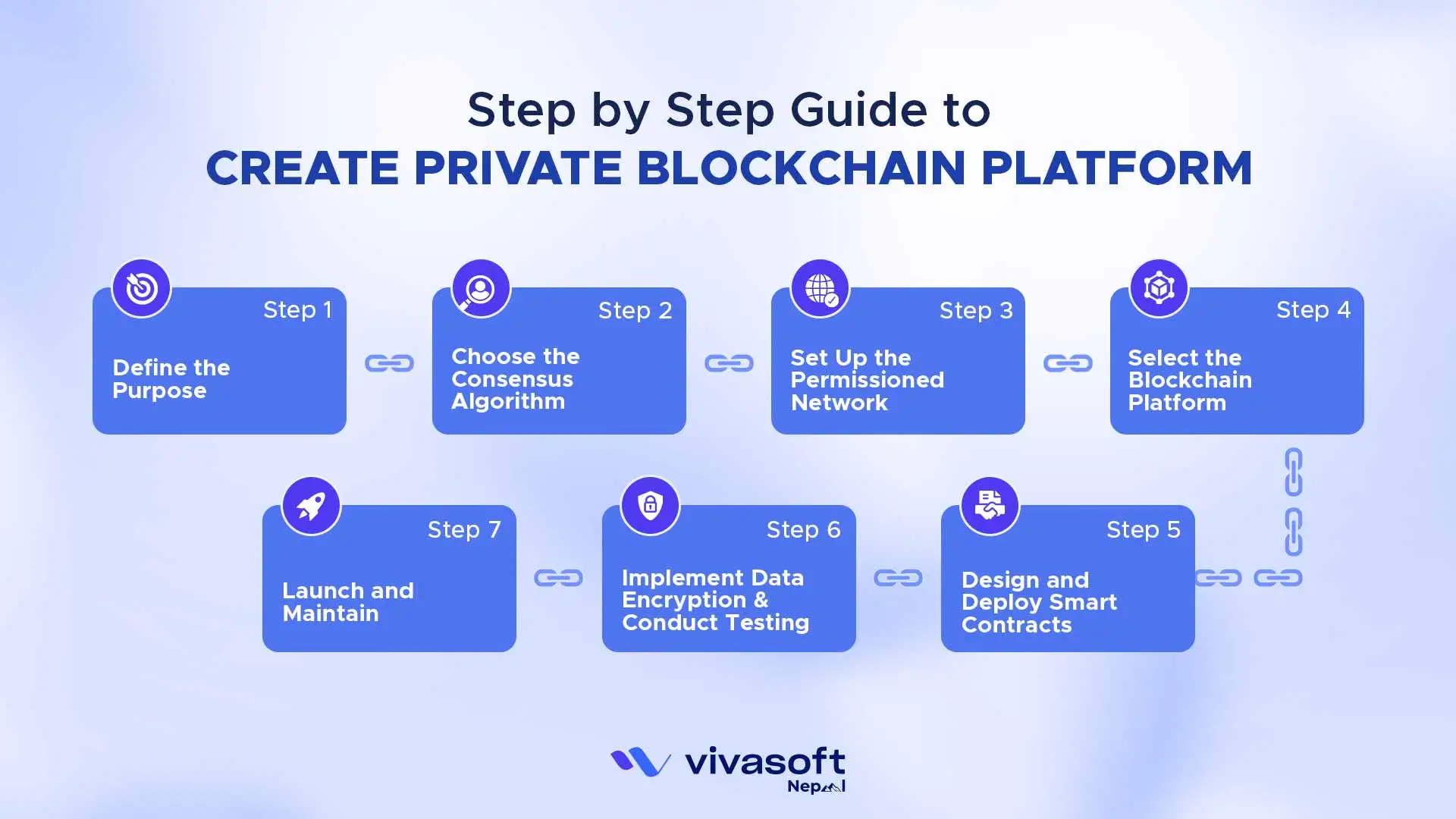
Step 1: Define the Purpose
The first step is to understand why your organization needs a blockchain? A clear purpose guides all your technical decisions later. Determine what issue it will help solve and what objective it should achieve. This understandability assists you to plan the network, choose the right smart contracts and the right consensus algorithm to fit your needs.
Step 2: Choose the Consensus Algorithm
The consensus algorithm is what keeps all member of your blockchain network on the same track. It ensures all participants agree on which transactions are valid. There are several popular options to consider:
- RAFT: Fast and reliable for smaller networks.
- PBFT (Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance): Ensures safety even if some nodes misbehave.
- IBFT / IBFT2: Ethereum based option designed for permissioned networks.
- Proof of Authority (PoA): Uses trusted validators to sign blocks making it perfect for enterprise environments.
The algorithm you pick affects how fast and secure your transactions are.
Step 3: Set Up the Permissioned Network
Now it’s time to develop your network. Set up nodes, peers, orderers and certificate authorities (CAs). Assign role using role-based access control (RBAC) and secure communication with TLS encryption. Key storage can be handled by HSMs or cloud KMS solutions. A well structured setup ensures your network is both secure and efficient right from the start.
Step 4: Select the Blockchain Platform
Choose a platform based on your requirements :
- Hyperledger Fabric: Offers modular design, private channels and chaincode for enterprise workflows.
- Quorum: Ethereum-based and privacy-focused which is perfect for finance.
- R3 Corda: Optimized for regulated industries.
- MultiChain: Lightweight and simple to deploy.
Consider developer support and programming languages such as Go, Java, Solidity or JavaScript for building applications.
Step 5: Design and Deploy Smart Contracts
Smart contracts do the work for you like sharing data, approving payments or handling deals. Write and test contracts, deploy them with CLI devices or SDKs. Make sure they follow your network’s access control policies and only allow authorized actions.
Step 6: Implement Data Encryption & Conduct Testing
Encrypt what matters most. Use AES or RSA to keep data safe. Store large files off-chain in places like IPFS. Test everything first in a sandbox network. Watch how it performs, how fast it moves and how it handles pressure. Check for security gaps, ensure smart contracts respect access rules and run multiple tests to catch errors early. Fix issues before going live.
Step 7: Launch and Maintain
Once testing is completed go live! Monitor nodes, block production and overall network health. Update chaincode and policies as needed. Keep backups, plan upgrades and monitor the system using tools such as Prometheus or Grafana. A blockchain is a living system, it will remain strong as long as you continue taking care of it.
How Does a Private Blockchain Work?
Private blockchains work in a step by step process in order to ensure the security of the data and the reliability of the network. All operations are well controlled to ensure that only the authorized parties are allowed to communicate with each other and ensure that the transactions are done properly.
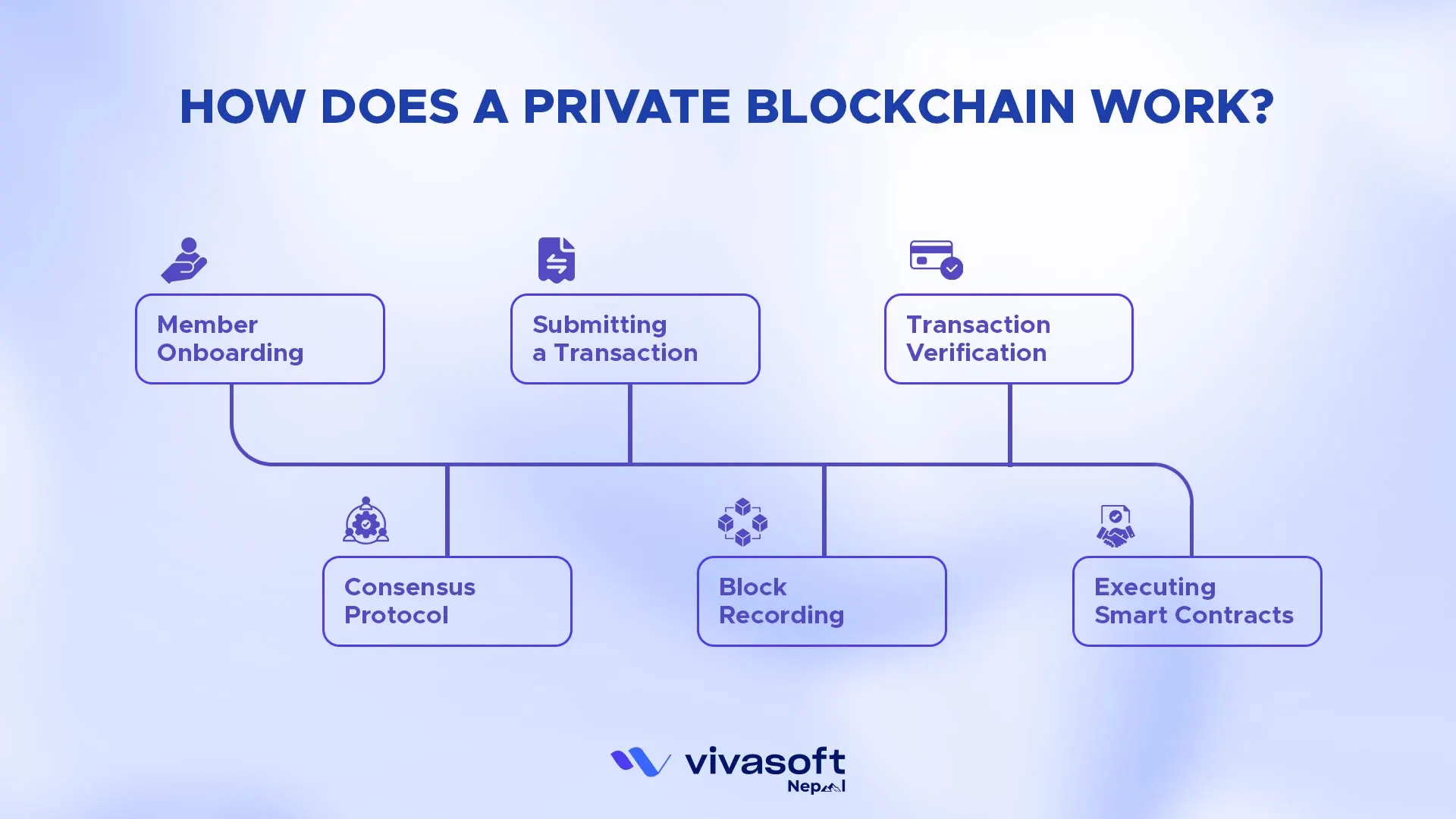
- Member Onboarding: New members are authenticated using X.509 certificates and the members are registered to the network.
- Submitting a Transaction: Transactions request is sent by authorized clients via SDKs or API gateways.
- Transaction Verification: The peers confirm every transaction according to ACLs and network policies.
- Consensus Protocol: Nodes agree on transaction order using RAFT, PBFT, IBFT or PoA.
- Block Recording: Verified transactions are combined into blocks and they are connected to Merkle roots and appended to the ledger.
- Executing Smart Contracts: There are pre-established contracts that automatically apply business rules to the network.
What Are the Advantages of Private Blockchains?
Private blockchains come with a number of advantages for businesses. Let’s take a look at some of the key advantages they provide.
- Enhanced Data Security: Only authorized participants can access sensitive data.
- Faster Transactions: The network will be permissioned which means that transactions will be approved fast and will not take as much time.
- Cost Savings: Automation of processes reduces workload and errors.
- Traceability: All the transactions are documented and may be reviewed by the authorized parties which simplifies accountability.
- Custom Governance: The companies have the ability to establish their rules, roles and policies. They can adjust the blockchain to their requirements.
- Scalability and Compliance: The networks can grow with business needs and regulatory demands.
What Are the Challenges of Private Blockchains?
There are numerous advantages of the private blockchains but they also come with some challenges that companies must consider before adopting them. Here are some of them :
- Centralization Risk: With only a few participants, the network is less decentralized. So a small group has more control.
- Security Vulnerabilities: The setup errors or bugs in software can put sensitive information at risk even inside the network.
- Less Transparency: Only authorized members can see the entire ledger. Hence an outsider cannot view the transactions.
- Complexity of Integration: It may require additional planning and work to add a private blockchain to existing systems or integrate it with other blockchains.
- Cost and Complexity: It is not that easy to set up and maintain a private blockchain. It will require experienced individuals and resources to run it efficiently.
Build a Private Blockchain for Your Business with Vivasoft Nepal
As blockchain technology continues to transform industries, having the right development partner is key. Vivasoft Nepal is a top private blockchain solution provider. They help businesses create secure, permissioned networks. This streamlines operations and protects sensitive data.
The team focuses on creating complete blockchain solutions. This includes architecture design, setting up consensus and implementing smart contracts. They also integrate these solutions with existing systems. Whether you’re a start-up who’s just discovering blockchain for the first time or a business ready to modernize data infrastructure, Vivasoft Nepal provides the technical skills and long-term assistance you need.
FAQs
What are the top use cases and industries suitable for private blockchain deployment?
Private blockchains are suitable for finance, supply chain, healthcare, insurance and government sector where security, privacy and compliance are the essential factors.
Which consensus algorithms are commonly used in private blockchains and why?
PBFT, RAFT and PoA are popular choices. They are selected because they are fast, error tolerant and appropriate to the networks with a known set of participants.
How to integrate a private blockchain with existing enterprise systems or legacy databases?
The process of integrating with the blockchain includes APIs, middleware or connector usage that enables sharing of data between blockchain nodes and legacy systems and provides smooth interoperability.
What is the typical cost and time estimate for deploying a private blockchain solution?
The typical cost to deploy a private blockchain solution usually ranges from $10,000 to $500,000 . This range depends on factors like scale and complexity. Building it takes 2 to 12 months from a simple MVP to a full enterprise solution.













