The retail world is undergoing a massive digital change, with the growing adoption of blockchain technology transforming supply chains. The market size is likely expanding continuously with the flow of increased investments and digital innovation. The retail blockchain market size was valued at USD 0.72 billion in 2025. Moreover, it is expected to reach around USD 6.01 billion by 2030. It is at a CAGR of 52.92% during 2025–2030.
One of the notable trends gaining popularity in this growth is tokenized loyalty programs. Shoppers are getting digital points or tokens that can be used like real money. At the same time, automated supply chains use smart contracts to instantly release payments to suppliers once goods are delivered, reducing delays and costly mistakes.
Top retailers like Walmart and Alibaba are already using these systems and experiencing amazing results, including faster transactions and stronger customer loyalty. Read on to get a detailed overview of how blockchain turns a complex supply chain into a smooth and digital engine.
What is Blockchain in the Retail Market?
The blockchain in the retail market is a specialized digital system used to optimize retail operations. Businesses mainly utilize decentralized ledgers to secure data and track products. The main goal is to prevent fraud and improve supply chain clarity.
|The usability of this tech in the industry is increasing notably. This is mainly due to its improved transparency and amazing efficiency, which help modern retail businesses reach their ROI goal. Retailers can verify product authenticity, manage inventory, and even secure customer data.
The fully audited smart contracts are automating vendor agreements and compliance tasks. Therefore business can build customer trust in days that took years before. For example, Amazon has utilized blockchain to track shipments from manufacturers to warehouses, ensuring accurate delivery and preventing counterfeit goods.
What Are the Benefits of Blockchain in Retail?
Blockchain has been successfully solving many deep-rooted retail issues. Businesses are using it as a digital map to track every product and dollar. This technology builds a stronger and safer future for global shopping experiences. It helps enhance brand reputation. Here is more you can expect:
1. End-to-End Supply Chain Traceability
Blockchain helps track goods from the raw material stage to the shelf. Each transfer is recorded permanently, and there is no chance of altering it. Retailers are utilizing blockchain for sustainability. This makes it easy to find delays and prevent tampering. They are able to guarantee their customer base that items are fresh and ethically sourced. All in all, this helps build confidence in customers about product quality and origin.
2. Anti-Counterfeiting & Brand Protection
Through blockchain platforms, luxury brands are getting unique IDs that help prove brand authenticity. These records live on a secure network. Customers can scan a code to verify their purchase instantly. Beyond just protecting brands from fake goods entering the market, it enhances trust and brand value.
3. Payment Processing Cost Reduction
In traditional transaction methods, there are many middle layers and high fees. Blockchain makes it possible to have direct transfers between the buyer and the seller. This reduces transaction fees and, most importantly, shortens settlement time. At the same time, shoppers can take advantage of faster checkouts and fewer payment delays. It creates a smoother purchasing experience overall.
4. Customer Trust & Transparency
Shoppers always demand clarity to know where their clothes and food come from when they are shopping. Blockchain offers clear and verified information about a product’s origin and journey. Every detail is recorded securely, through which brands can prove claims about quality. This level of transparency helps shoppers make informed choices and builds credibility for brands.
5. Smart Contract Automation
Smart contracts are designed with pre-set rules that automatically complete actions without the need for human intervention. This offers flexibility and reliability, such as releasing payments to suppliers once a delivery arrives. It removes manual paperwork and human error. Most notably, business operations become faster and much more reliable.
6. Fraud Prevention & Data Security
Centralized databases are easy targets for hackers and data leaks. Instead of storing information in one central database, blockchain helps distribute data across multiple secure nodes. Each record is encrypted and requires network approval for any alteration. This structure makes hacking extremely difficult and reduces fraudulent activities. Businesses can protect sensitive information more effectively.
7. More Transparent Loyalty and Rewards Systems
Traditional loyalty programs are often fragmented and difficult to manage. Points may disappear, records become inconsistent, and customers struggle to track rewards.
Blockchain turns loyalty points into secure, verifiable digital assets. Transactions are transparent, tamper resistant, and easier to manage for both retailers and customers. This builds trust while simplifying program administration.
8. Reduced Operational Costs
Retail systems frequently rely on overlapping databases, third party verification, and manual reconciliation. Over time, these inefficiencies drive up operational expenses.
Blockchain consolidates record keeping into a shared system, automates verification, and reduces reliance on intermediaries. Fewer errors, faster processes, and streamlined workflows translate into measurable cost savings.
How Blockchain Works in the Retail Industry?
Here’s a simplified walkthrough of how blockchain can operate behind the scenes in retail.
Step 1: A Product or Transaction Enters the Blockchain Record
When a product is manufactured, shipped or sold, the relevant transaction gets recorded on the blockchain. For example: “Farm harvested apples” or “Supplier shipped batch #123 to Warehouse A” or “Store sold item #SKU -789 to Customer X.”
Step 2: Data Gets Distributed Across Retail Stakeholders
Instead of one company controlling a central database, the blockchain ledger is shared across everyone involved suppliers, logistics teams, retailers even regulators. Everyone sees the same synced data which keeps things consistent and cuts out those usual information silos.
Step 3: Smart Contracts Automate Approvals, Inventory & Payments
Smart contracts are basically self executing programs on the blockchain that handle a lot of routine work by themselves. For instance, when a shipment reaches the warehouse; it can auto-trigger a payment or if inventory drops below a set level, it can create a restock order and even sort out supplier invoices without any person doing it manually.
Step 4: Real-Time, Tamper-Proof Updates Across All Channels
Since the ledger is shared across the network updates sync almost in real-time. And once a transaction is written to the chain, you can’t just modify it without network consensus. This keeps the entire record like manufacturing, shipping, receiving and sales, secure and pretty much tamper-proof.
Step 5: Customers Access Transparency
At the end of the chain, when you buy the product retailers can give customers access to the blockchain record (e.g. via QR code, app or digital label). That means a shopper can see where the product came from, who handled it and its whole journey which boost the trust and confidence.
Use Cases of Blockchain in Retail
Blockchain offers a range of use cases in retail. Here are some of the most promising ones:
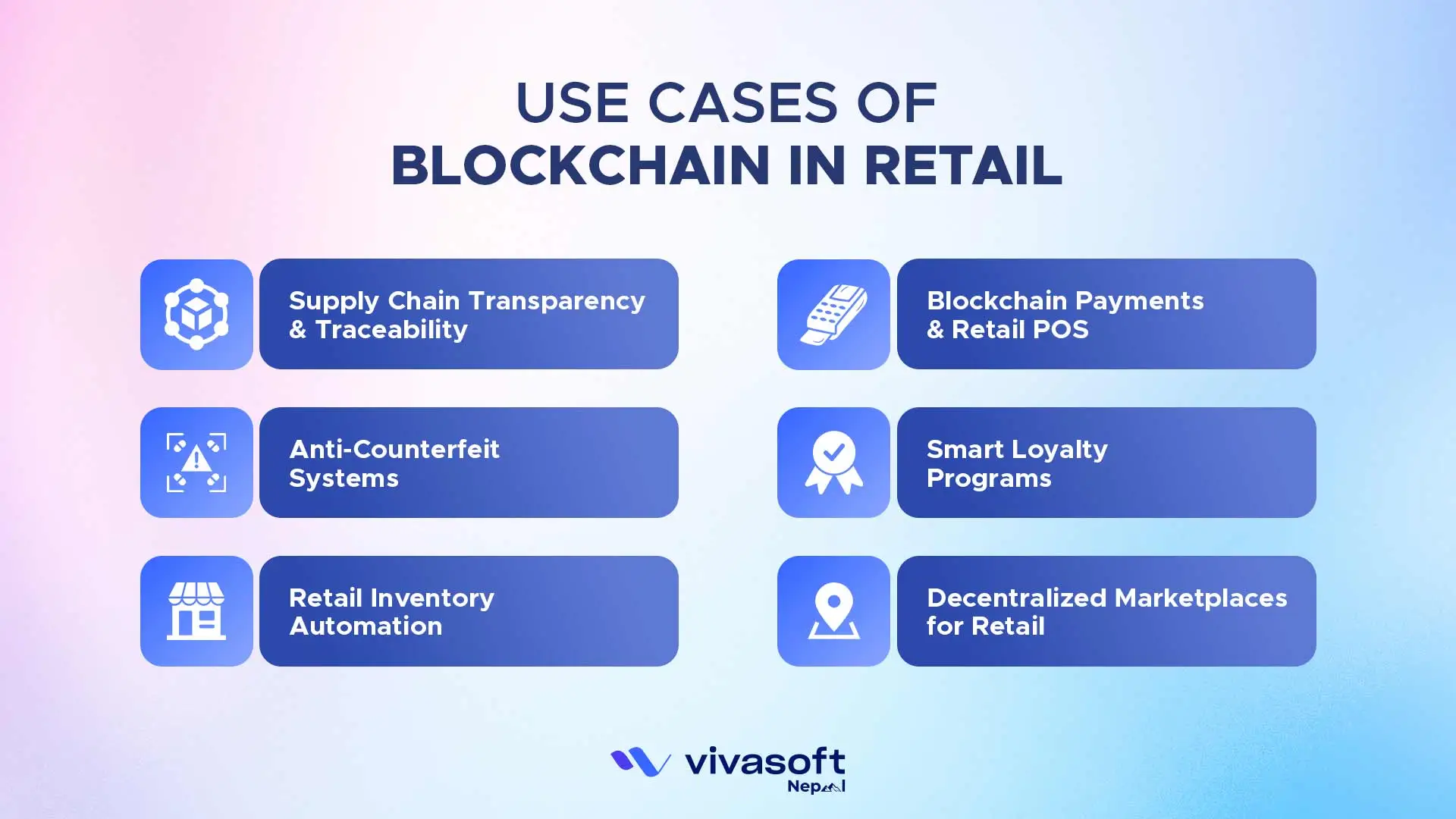
Supply Chain Transparency & Traceability
Supply chains can be long and confusing with products moving through many hands before reaching the store. Blockchain help to keep track of everything so both retailers and customers can see what’s going on at each step.
- Food safety: Blockchain let retailers trace food quickly if there’s a contamination or recall. This way harmful products can be removed before they reach shoppers, this keeps everyone safe.
- Perishables: Fresh foods, medicines or other time-sensitive goods can be tracked for harvest dates, expiry dates and storage conditions. This make sure nothing goes bad unnoticed or gets misplaced along the way.
- High-value goods: Expensive items such as diamonds, luxury bags or electronic get their whole journey recorded on the blockchain. It helps buyers trust that they are getting the real thing and not a counterfeit.
Anti-Counterfeit Systems
Blockchain makes it way harder for fake products to enter the supply chain because every item has a traceable digital identity. Brands can prove authenticity without needing complicated verification steps.
- Fashion, luxury goods: Blockchain -backed digital labels or certificates ensure that expensive bags, watches, clothing are authentic reducing fake resale or counterfeits.
- Electronics: Serial numbers and blockchain records help verify genuine devices, components and spare parts.
- Beauty products: Customers can verify ingredient sourcing, manufacturing batch and authenticity.
Retail Inventory Automation
Blockchain helps retailers monitor stock levels more accurately and avoid mistakes from manual updates. It can sync inventory changes across warehouses, stores and suppliers almost instantly.
- Real-time counts: When a product move from the warehouse to shelves or get sold the inventory ledger updates automatically.
- Overstock prevention: Smart contracts and live tracking can help stop overstocking or running out by triggering orders when stock gets low.
Blockchain Payments & Retail POS
Some retailers are experimenting with blockchain-based payments to speed transactions and reduce fee. It’s still early but stores are exploring systems that connect crypto wallets to regular POS machines.
- Crypto payments in retail stores: Customers can pay using digital currencies through QR code or wallet apps.
- Pros & cons of crypto payments: Pros include fast settlement, lower fees and transparency ; cons include volatility, regulatory uncertainty and limited adoption.
- Retail POS systems that accept blockchain: Some modern POS tools integrate crypto gateways for hybrid payment options though adoption is still experimental.
Smart Loyalty Programs
Blockchain helps make loyalty systems more flexible and less prone to misuse. Customers get rewards that feel more valuable because they’re token-based and fully traceable.
- Tokenized rewards: Points can be issued as digital tokens that work across multiple brands.
- Fraud-proof points: Transactions are recorded on-chain which reduces fake or duplicated points.
Decentralized Marketplaces for Retail
Blockchain enables marketplaces where buyers and sellers interact directly without middle platforms taking a big cut. It also makes product histories more transparent which builds more trust.
- Peer-to-peer commerce: Shoppers can buy directly from sellers with blockchain handling the transaction.
- Transparent product histories: Each item carries its own traceable record, helping customers know what they’re buying.
What Are the Challenges of Using Blockchain in Retail Industry?
Blockchain brings transparency and speed to retail, but adopting it isn’t as easy as it sounds. Most retailers discover a few practical roadblocks once they try implementing it.
Integration With Existing Retail Systems (POS, ERP, WMS)
Many retailers already use complex legacy systems : point-of-sale (POS), enterprise resource planning (ERP), warehouse management (WMS) and inventory software. Integrating blockchain with those existing systems while maintaining proper data flow, compatibility and reliability is often difficult and costly process.
High Initial Investment & Training
Setting up blockchain isn’t cheap. Retailers must invest in infrastructure, skilled developers and staff training. For many, the upfront cost feels high compared to the short-term return so adoption slows down.
Data Standardization Across Supply Chains
Blockchain only works smoothly when every supply-chain partner follows the same data format. But suppliers, shippers and retailer all use different systems. Getting everyone on one standard becomes a major bottleneck.
Lack of Technical Expertise
There is still a limited pool of blockchain talent, especially for enterprise-level projects. Many retail teams lack in-house expertise, so they hire a blockchain development company to manage development, integration, and long-term support, while ensuring scalability and security.
Regulatory & Compliance Complexity
Retail regulations vary widely and blockchain introduces questions around data privacy, smart contract legality and cross-border data flow. Navigating all of this takes time and slows adoption.
Blockchain Success Stories in the Retail Industry
Here are some real-world examples of major companies using blockchain in retail or supply-chain operations :
- Walmart: Walmart, in partnership with IBM, uses blockchain to trace produce, cutting recall times drastically. What used to take days to track can now be done in seconds, making food safety faster and more reliable.
- Carrefour: Carrefour deployed blockchain to track agricultural products. Customers can now see where food comes from, how it’s handled and its full transit history which is becoming common among big food retailers.
- Amazon: Amazon offer blockchain solutions through its cloud services that retailers can use to improve inventory management, tracking and backend logistics. These scalable, managed networks help make operations smoother and more automated.
- Alibaba: Alibaba leverages blockchain to verify product origins and reduce counterfeit goods. This is particularly useful for luxury items, electronics and other consumer products sold on its platform.
- De Beers: De Beers uses its blockchain platform, Tracr, to track diamonds from mine to market. This ensures conflict -free sourcing and proves the authenticity of each stone.
- American Express: American Express explores blockchain-based tokenized rewards to optimize loyalty programs. This allows more flexible and secure ways for customers to earn and redeem rewards though public examples are still emerging.
- Walgreens & P&G: In pharmaceuticals and consumer health, these companies use blockchain to track the origin, batch and safety of over-the-counter products. This improves recall management and build customer trust.
Conclusion
Retail is slowly moving into a new era and blockchain is right in the middle of it. From tracking products end-to-end, automating payments and keeping inventory in check to cutting down on counterfeits. Blockchain is giving retailers tool to run things smarter and more smoothly. For shoppers, it means more trust and clarity ; for businesses, better insights and easier operations.
For businesses wanting to explore blockchain technology more, working with trusted blockchain technology partners can make the process a lot easier and help unlock its full potential. They don’t just help connect blockchain to existing systems, they also make sure security, compliance and scalability are handled, so the transition goes smoother and feels less overwhelming.
FAQs
What industries use blockchain the most?
Blockchain is heavily used in finance for payments and settlements, in supply chain for tracking goods, in healthcare for secure data sharing and in retail for transparency and inventory accuracy. It’s also growing fast in gaming, identity management and asset tokenization.
How is blockchain used in retail fashion industries?
Blockchain is used in retail fashion to track products across the supply chain, verify authenticity, prevent counterfeiting, and support sustainability claims. It also helps brands manage inventory better, enable secure resale, and improve customer trust through transparent product information.
Is blockchain secure for retail payments?
Yes. Blockchain -based payments use encryption, distributed validation and tamper-resistant records which makes them highly secure. They also settle faster than traditional methods and reduce the chances of chargebacks or fraud.
Does blockchain reduce retail costs?
Yes, by automating verification, reducing paperwork, cutting down fake product losses and improving inventory accuracy, blockchain helps retailer save both time and operational costs.













