Blockchain ecommerce platform development means creating an online store or marketplace using blockchain technology rather than a fully centralized system. Instead of keeping all data on one server, things like transactions, payments and order records are stored on a distributed ledger. Smart contracts are used to automate actions such as releasing payments or confirming orders which reduces manual work and errors.
Many businesses are now moving toward decentralized; blockchain-powered marketplaces because traditional ecommerce platforms still face issues with security, scaling and trust. Problems like data breaches, slow cross-border payments and platform dependency push companies to look for better alternatives. With blockchain commerce, businesses get stronger security, global scalability and a foundation that fits well with Web3 commerce and future digital models.
What is a Blockchain Ecommerce Platform?
A blockchain ecommerce platform is a digital commerce system where product listings, transactions, reviews, payments and even identities are recorded on a blockchain network. Instead of relying on a central authority, data is distributed across multiple nodes which makes manipulation extremely difficult. Smart contracts automate business rules such as payments, refunds and order fulfillment without a human intervention.
The main difference between blockchain-based and traditional ecommerce architecture is control and trust. Traditional platforms store data in a centralized servers and require users to trust the platform owner. With blockchain in ecommerce, records are shared across a network and cannot be easily changed once verified. This adds a higher level of security, improves data integrity and builds trust between buyers and sellers. Decentralization also reduces single points of failure making the ecommerce platform more resilient and a reliable over time.
Key Features of a Blockchain Ecommerce Platform
A blockchain ecommerce platform isn’t just a normal online store. It has some features that make buying, selling, and payments safer, faster, and easier to trust.
- Smart Contract Escrow: Payments are held automatically in a smart contract until both buyer and seller finish the deal. No need for middlemen and it helps avoid fraud. Money only moves when everything is done.
- Crypto & Stablecoin Payments: People can pay with crypto or stablecoins. It’s faster and cheaper than using banks. Stablecoins also don’t swing in price too much and still use blockchain security.
- NFT Authenticity Certificates: Products, especially luxury or digital stuff, can be linked to an NFT. Buyers can check if it’s real or not instantly. It helps prevent fakes and builds trust.
- Tokenized Loyalty Programs: Customers get tokens instead of normal points. Tokens can be used across vendors or redeemed for rewards. It make loyalty programs more flexible and valuable.
- KYC Identity Verification: Users verify themselves securely on the blockchain. Sensitive information isn’t shared everywhere. Helps reduce fraud and keeps things compliant.
- On-Chain Reviews: Reviews are stored on the blockchain and can’t be deleted or faked. They are linked to real transactions. This makes feedback more trustworthy for future buyers.
- Multi-Vendor Scalability: Multiple sellers can work on the same platform safely. Each seller’s data is separate and the system can handle more vendors easily. This lets the platform grow without slowing down.
Why Is Blockchain Needed in Ecommerce?
Modern ecommerce platforms face trust, cost, and transparency issues that centralized systems struggle to fix. Blockchain in ecommerce directly addresses these gaps.
Fake Reviews & Counterfeit Products
Fake reviews and copied product listings are common issues in ecommerce and they slowly break customer trust. With blockchain-based or decentralized reviews, feedback is stored on-chain and cannot be edited or removed later. Blockchain records and NFTs can also be used for product authentication; making it easier to verify originality, especially for luxury, branded or high-value items.
High Transaction Fees & Delays
Traditional payment systems often involve multiple intermediaries which leads to higher fees and slow settlement times. This becomes even more painful for the international transactions. Blockchain ecommerce allows businesses to accept crypto and stablecoin payments directly, which reduces transaction costs and enabling faster, near-instant settlements across borders.
Limited Supply Chain Transparency
Most ecommerce platforms offers a very limited visibility into where products come from or how they move through the supply chain. Blockchain enables end-to-end supply chain tracking where every step is recorded and verified. This improves transparency and trust; especially in industries like food, retail and a logistics.
Data Breaches & Privacy Risks
Centralized ecommerce databases are a common target for cyberattacks and data leaks. With a secure ecommerce architecture using blockchain, data is distributed instead of stored in a single location and identities can be encrypted or managed through decentralized identity systems. This significantly lower the risk of breaches while giving users better control over their own data.
What Are the Challenges of Blockchain in Ecommerce?
Blockchain sounds great on paper but in real ecommerce projects, it does come with some problems. These are things which most businesses run into when they start looking at blockchain seriously.
- Regulatory restrictions: Crypto rules change from country to country. What works in one place may not be allowed in another. Because of this companies usually need extra time to understand laws before launching anything.
- Web3 wallet usability issues: For many users, Web3 wallets are still confusing. Setting them up, saving private keys or paying with crypto isn’t something everyone is comfortable with yet.
- Scalability of public chains: Public blockchains can slow down when traffic increases. During busy hours, transactions may take longer and fees can suddenly rise, which isn’t ideal for ecommerce.
- Initial development cost: Blockchain ecommerce platforms usually cost more in the beginning. Smart contracts, blockchain integration and security audits all add up fast.
- Consumer awareness & adoption: Most shoppers are still new to decentralized commerce. If people don’t really understand how it works; they might hesitate to trust it or even try using the platform at first.
How Blockchain Solves Ecommerce Challenges?
Blockchain helps ecommerce platforms fix problems that have existed for years. Instead of relying on manual checks or centralized systems; it uses automation, transparency and decentralization to make things works better.
Smart Contracts for Automated Transactions
One common challenge in ecommerce is manual payment handling, refunds and disputes. These processes takes time and often cause errors or delays.
Smart contracts solve this by managing payments, refunds and order processing automatically. Once conditions like delivery confirmation are met, transactions are completed without third parties. For example; in a marketplace, buyer funds can stay locked in a smart contract until delivery. If a return happens, refunds can be triggered automatically, keeping things fair for both sides.
Transparent Product Tracking
Many ecommerce platforms struggle with product traceability. Customers usually don’t know where products come from or how they move through the supply chain.
Blockchain records each step of a product’s journey on a shared ledger. These records are permanent and can’t be changed which improves transparency across the supply chain. This helps businesses track sourcing, manufacturing and delivery more clearly. Many ecommerce brands already rely on blockchain in retail and supply tracking to show customers product origin and movement.
Faster Cross-Border Payments with Crypto
Cross-border payments are often slow and expensive because they depend on banks and multiple intermediaries. This creates delays for sellers and higher costs for buyers.
Blockchain-based payments allow businesses to accept crypto or stablecoins directly. For global sellers, this means getting paid in minutes instead of days. It also reduces currency conversion issues and improves cash flow for international ecommerce platforms.
Decentralized Identity (KYC) for Sellers & Buyers
Identity verification is another challenge in ecommerce. Users are often asked to upload the same documents on multiple platforms, increasing friction and data risks.
Blockchain-based KYC allows users to verify their identity once and reuse it securely. Users stay in control of their data while platforms remain compliant. This reduce fraud, speeds up onboarding and lowers risk of data exposure.
Anti-Fake Review System
Fake reviews are a major trust issue in ecommerce. On centralized platforms, reviews can be edited, removed or even manipulated.
Blockchain solves this by storing reviews on-chain and linking them directly to verified purchases. Only real buyers can leave feedback and reviews stay unchanged. Over time, this builds more honest reviews and improves buyer trust in the platform.
How is a Blockchain-Based Ecommerce Platform Developed?
Building a blockchain-based ecommerce platform isn’t just about coding a site; it’s about making a system that actually works, stays secure and can handle all the blockchain stuff like smart contracts and crypto payments. If you’re a business looking into blockchain for ecommerce, knowing the steps kind of helps you see what’s needed and what to focus on.
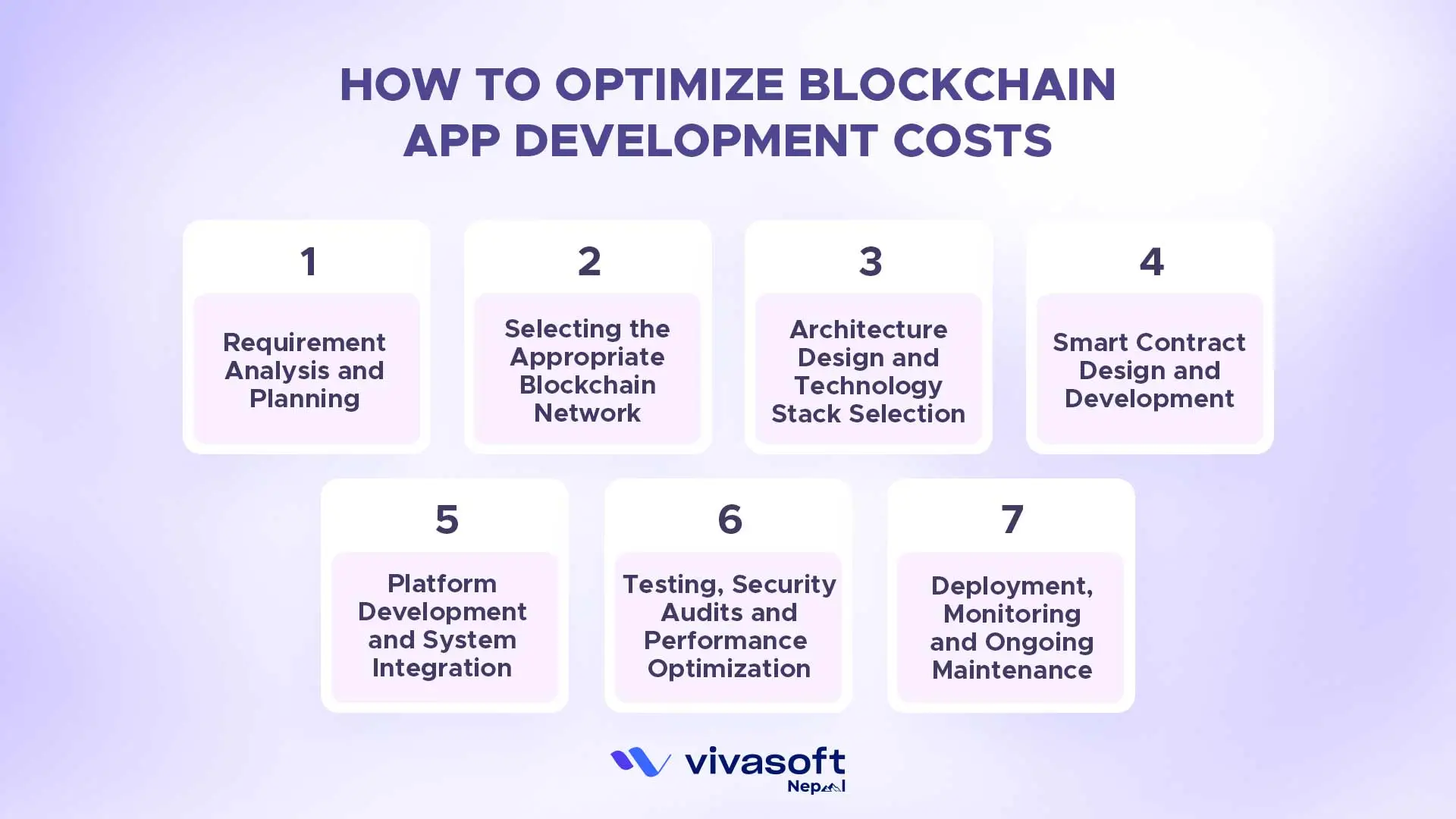
Step 1: Requirement Analysis and Planning
First, you need to figure out exactly what your platform is supposed to do. Are you building a B2C store, B2B platform, multi-vendor marketplace or something for digital goods or NFTs? Then decide the features like crypto payments, tokenized loyalty programs, decentralized reviews or supply chain tracking. This planning phase is super important because it sets the foundation for everything else. Skip this and the project can get messy later.
Step 2: Selecting the Appropriate Blockchain Network
Choosing the blockchain network is a big deal. Public chains like Ethereum or Solana give full decentralization and transparency but can have higher fees. Private or permissioned chains are faster and cheaper but less open. Some companies even go for a hybrid model to balance speed, security, and scalability. This decision affects smart contracts, transaction speed, and the platform’s overall performance.
Step 3: Architecture Design and Technology Stack Selection
Next, design the architecture. Decide which frontend and backend frameworks you’ll use, how wallets will be integrated, APIs for blockchain interaction and database setup. Pick the best programming languages and smart contract frameworks and plan how blockchain explorers will connect so users can verify transactions. A good tech stack is critical for smooth and a scalable platform.
Step 4: Smart Contract Design and Development
Smart contracts are like the brain of your blockchain ecommerce platform. They handle payments, escrow, refunds, loyalty rewards, all automatically. They need to be coded carefully because once they’re on the blockchain, fixing mistakes is hard. Security audits are essential at this stage to prevent exploits.
Step 5: Platform Development and System Integration
Now the platform itself is built. Product catalogs, shopping carts and checkout systems are created; then integrated with blockchain features like crypto wallets, NFT certificates, tokenized loyalty programs and decentralized identity. You also connect KYC systems, supply chain APIs and payment gateways so everything works together.
Step 6: Testing, Security Audits, and Performance Optimization
Before launch, test everything. Load testing checks if the platform can handle many users at the same time. Security audits are done for smart contracts and the whole system. Performance is optimized so blockchain transactions, wallet operations and API calls are fast and reliable.
Step 7: Deployment, Monitoring, and Ongoing Maintenance
Finally, launch the platform. But it doesn’t stop there; continuous monitoring is needed to fix bugs, add features and to maintain security. Upgrade smart contracts if needed and make sure the platform can scale with users and transactions. This keeps the ecommerce system stable, secure and ready for the growing world of Web3 commerce and decentralized marketplaces.
Estimating the cost of building the blockchain ecommerce platform can be a bit tricky. It usually depend on things like the features you want, how complex the platform is, the integrations involved and the tech stack you go with. So the costs can vary a lot but below is a rough idea of price ranges based on common project types.
How Much Does Blockchain Ecommerce Platform Development Cost?
| Type | Development Cost |
|---|---|
| Standard | $25,000 - $55,000 |
| Medium | $45,000 - $100,000 |
| Complex | $100,000 - $200,000++ |
These are rough estimates, and actual costs can vary depending on your project scope and features. For businesses looking at more advanced or enterprise-level solutions with complex blockchain integration, exploring enterprise blockchain solutions can help plan and execute the project more efficiently.
What Are the Factors Affecting the Cost of E‑commerce Platform Development?
Building a blockchain ecommerce platform can vary a lot in cost depending on what you want. There are several factors that directly impact development time, complexity and budget.
Blockchain Protocol Selection
The type of blockchain you choose make a big differences. Public blockchains like Ethereum can be more expensive because of gas fees and extra optimization work. Private or permissioned chains may be cheaper but offer less decentralization. Picking the right protocol affects speed, security and cost.
Platform Complexity and Scope
A simple online store costs less than a full multi-vendor marketplace with Web3 features. Adding features like subscriptions, memberships or digital goods marketplaces increases development effort and budget. The bigger the platform; the more time and resources it needs.
Key Features and Custom Integrations
Features like NFT certificates, crypto wallets, KYC verification and supply chain tracking add extra work. Each integration requires careful planning and testing, which raises costs. Customizing these features to fit your business needs also adds development time.
Development Team and Expertise
Experienced blockchain developers are usually more expensive but they can prevent costly mistakes later. Working with skilled teams like top blockchain development companies, ensures smart contracts and security are done right. This upfront investment save time and reduces risks in the long run.
Security Measures and Regulatory Compliance
Security audits, compliance checks and testing are essential but add to upfront costs. They prevent hacks, data breaches and regulatory fines. Skipping this can be cheaper initially but very expensive if problems occur later.
UX/UI Complexity
Making a blockchain platform simple for users is tricky. Balancing Web3 features with easy-to-use design requires extra design effort. A good user experience keeps customers happy and reduces confusion but it adds time and cost to the project.
Use Cases and Industry Applications of Blockchain-Based Ecommerce Platforms
Blockchain ecommerce platforms aren’t just an idea, they are already being used in different industries. From luxury goods to digital marketplaces, businesses are finding real ways to fix old problems.
Fashion and Luxury Goods
Counterfeit products are a huge problem in fashion and luxury. Blockchain lets brands use NFT-based authenticity certificates to prove ownership and stop fakes. For example, a designer handbag can have a digital certificate that anyone can check which helps buyers trust the product and protects the brand.
Food and Agriculture
Food safety and traceability are always tricky. With blockchain, every step of the supply chain is recorded; giving full transparency. Customers can see exactly where their food came from and companies can quickly find problems if something goes wrong which also helps with safety rules and compliance.
Digital Goods and NFTs
Digital stuff like art, music, or software can be hard to own safely. Blockchain works well for digital ownership, subscriptions, and creator marketplaces, where NFTs prove a buyer actually owns the item. It also helps creators sell safely and reduces fraud.
Cross-Border Trade
International payments are usually slow and expensive. Blockchain makes it easier by letting businesses accept crypto and stablecoins, cutting fees and making payments faster. Sellers anywhere can get paid almost instantly which helps cash flow and smooths global trade.
Subscription and Membership Models
Managing subscriptions or memberships can be messy on normal platforms. Blockchain allows tokenized subscriptions where smart contracts handle payments and access automatically. This makes billing clearer, easier to manage and reduces mistakes.
The Future of E‑commerce in Blockchain
Blockchain ecommerce is still early but it’s moving in that direction slowly. Over the next few years, more businesses will test it, learn from it and use it where it actually makes sense.
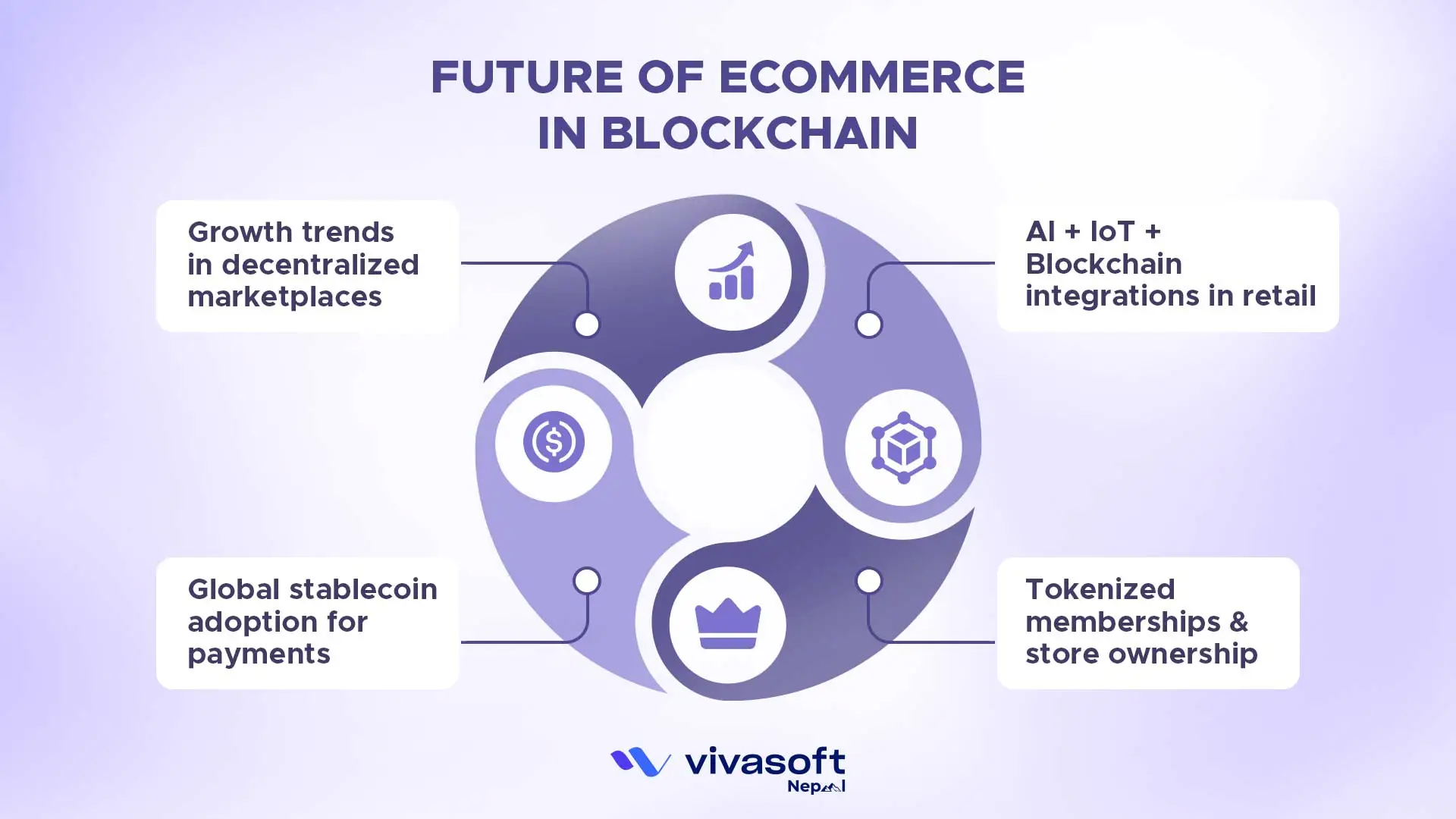
Growth Trends in Decentralized Marketplaces
Many brands don’t want to depend fully on big platforms anymore. Decentralized marketplaces give them more control over their store, data and customers. This trend will grow as businesses look for more freedom.
AI + IoT + Blockchain Integrations in Retail
Retail is getting smarter with time. When AI, IoT and blockchain are used together, supply chains become easier to track and manage. It also helps stores offer more personalized shopping, based on real data.
Global Stablecoin Adoption for Payments
Stablecoins are easier to use than normal crypto because prices don’t change much. Over time, more ecommerce platforms will accept stablecoins for daily payments. This could make online payments faster and cheaper.
Tokenized Memberships & Store Ownership
In the future, customers may do more than just buy products. They might hold tokens that give them access, rewards, or even a small ownership in a store. This can change how platforms are run and how loyal customers feel.
Conclusion
Blockchain is bringing real change to e‑commerce by solving issues like trust, fake reviews, slow payments, and lack of transparency. With features like smart contracts, crypto payments, on-chain reviews, and decentralized identity, businesses can build platforms that are more secure and fair for both buyers and sellers. While there are challenges like cost, regulations, and user adoption, the long-term benefits make blockchain worth exploring for future-ready e‑commerce brands.
For businesses exploring blockchain-based e‑commerce, having the right technical expertise makes a significant difference. Partnering with a professional blockchain development company can help reduce risks, manage complexity, and build a platform that is secure, scalable, and ready for long-term growth. Leveraging such expertise ensures a smoother development process and helps businesses fully unlock blockchain’s potential.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can blockchain ecommerce integrate with existing platforms?
Yes. Blockchain ecommerce can integrate with existing platforms like Shopify, Magento, or custom systems using APIs and middleware. Blockchain usually handles payments, smart contracts, or tracking, while the main store UI stays the same.
How does blockchain handle returns and refunds in ecommerce?
Returns and refunds are managed through smart contracts. The contract defines rules in advance, such as refund timelines or return confirmation. Once conditions are met, refunds are processed automatically without manual approval.
What programming languages are best for building blockchain ecommerce smart contracts?
Solidity is the most common for Ethereum-based platforms. Rust is used for Solana and some Layer-1 chains. For Hyperledger Fabric, Go and Java are often used for chaincode development.
How do layer-2 solutions improve blockchain ecommerce performance?
Layer-2 solutions process transactions off the main blockchain and settle them later. This reduces congestion, lowers gas fees, and speeds up checkout and payments. Examples include Polygon, Arbitrum and Optimism.
Which industries benefit most from blockchain-based ecommerce platforms?
Industries like luxury goods, fashion, food supply, digital products, NFTs and cross-border trade benefit the most. These sectors need authenticity, transparency and secure global payments.
Is blockchain ecommerce suitable for small and mid-sized businesses?
Yes, but usually with a phased approach. SMBs often start with crypto payments, NFT loyalty programs, or supply tracking instead of full decentralization. Using Layer-2 chains helps keep costs manageable.
How do crypto payments work in blockchain ecommerce?
Customers pay using a crypto wallet instead of a bank or card. Payments are confirmed on the blockchain and sent directly to the merchant wallet. Stablecoins are commonly used to avoid price volatility.













