KYC, or Know Your Customer, helps verify who users really are. When used with blockchain, this process becomes safer because user data is stored and shared on a decentralized system. This system combines identifying customers, checking risks, and ongoing monitoring in a secure, tamper-proof way. Because of blockchain, onboarding new users is faster, and repeated document checks are reduced.
It also protects user privacy with unchangeable records and smart contracts. Banks and companies save time and money with automatic compliance and instant data updates.
In 2025, new trends like AI-powered fraud detection and continuous monitoring make blockchain KYC even better. As rules get stricter, blockchain offers a safer and easier way to verify identities everywhere.
Understanding Blockchain and KYC
Blockchain is a decentralized and secure digital system that records transactions and data across a distributed network of computers. It is an immutable ledger that makes the data tamper proof and easy to trace. KYC (Know Your Customer) is the process to verify customer identity. This process is also used to make sure users are not involved in illegal activities.
KYC combined with blockchain technology create a more secure and transparent system for identity verification. Blockchain in KYC is simply a decentralized process that securely stores, shares, and validates personal identity data. This system allows the use of verified data across institutions with user consent. Since the data is recorded on an immutable ledger, it can’t be altered or hacked.
What Are the Key Components of Blockchain KYC?
Blockchain KYC consists of three core elements:
Customer Identification Program (CIP)
CIP establishes who a person or business genuinely is prior to allowing financial transactions. On blockchain, user-provided identity data (e.g., name, ID, address) is hashed and stored immutably. For businesses, UBO data and registration documents are also encoded. After confirmation, this verification can be shared with other authorized entities, reducing duplication.
Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
CDD determines user risk by assessing their behavioral patterns, background details, and relationships. Blockchain uses smart contracts to put users into groups- basic, simple, or detailed checks. It checks things like location, transaction type, and job role. Risk scores update instantly using their identity and behavior data.
Ongoing Monitoring
This ensures risk profiles remain current, catching suspicious changes as they occur.
Using blockchain, institutions watch users closely to spot sudden money flows or risky contacts. Automated alerts flag anomalies, while human oversight confirms regulatory action, such as filing SARs.
How Does Blockchain Technology Work in the KYC Process?
The usual KYC process is slow, costly, repeats work, and risks data security because all data sits in one place. Blockchain changes the game with its secure, decentralized, and permanent ledger.
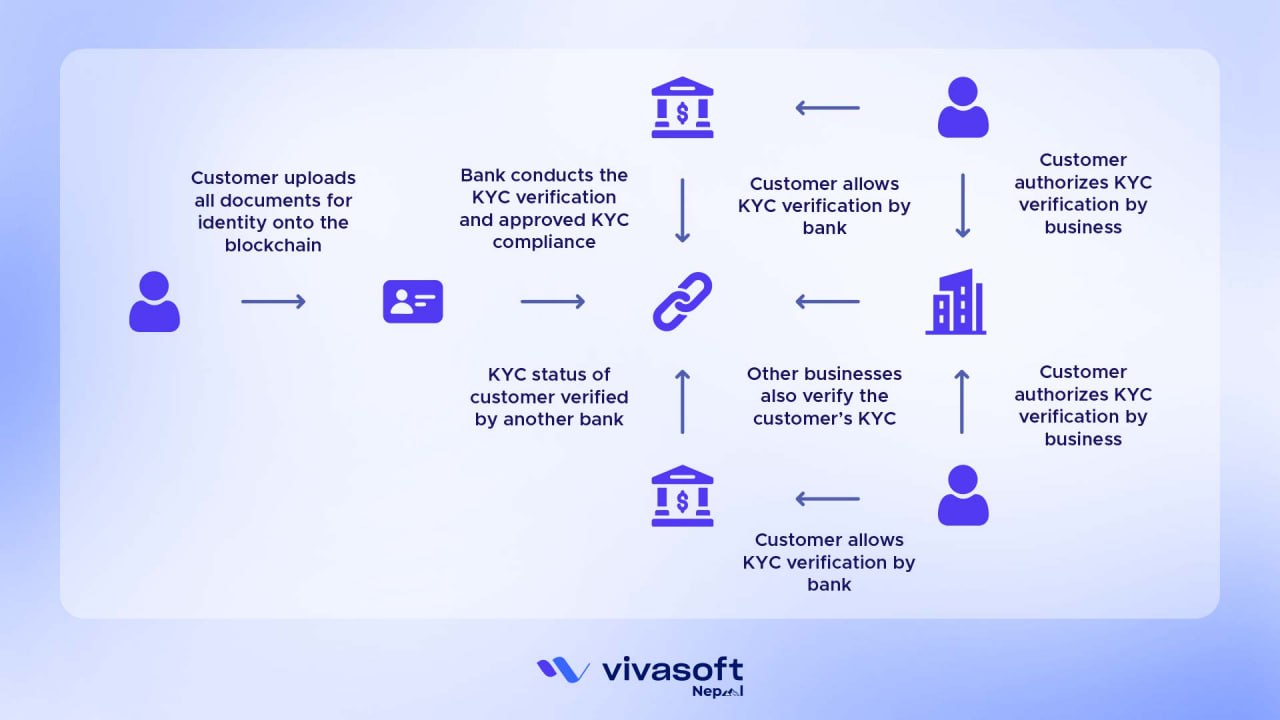
Step 1: User Signs Up and Shares Documents
First, the user signs up with a blockchain-enabled financial institution or KYC provider. After that, the user uploads ID documents such as a passport, driver’s license, or other official IDs. In regular systems, data is stored centrally and can be hacked. But blockchain works in a safer way.
- Secure Storage: The user’s data is stored safely—either encrypted on the blockchain or kept off-chain in a protected system, but linked through the blockchain.
- User Consent & Privacy: The system makes sure the user agrees before their data is used or shared, following rules like GDPR.
- Permission for Verification: FI1 asks for permission from the user to verify and handle the documents.
This first step builds trust. After verification, the data goes on the blockchain—and no one can secretly edit it.
Step 2: FI1 Checks Documents and Uploads a Digital Code
FI1 then checks the documents:
- It confirms if the documents are real and match official records.
It looks for signs of fake or edited information. - It verifies the data with trusted sources, if possible.
Instead of saving the full documents on the blockchain, FI1 creates a hash- a digital fingerprint of the verified data using a cryptographic formula like SHA-256.
- Changing just one detail changes the entire hash.
- This hash is uploaded to the blockchain to prove the documents were verified.
- The actual documents are stored securely off-chain by FI1, linked to the blockchain record.
Step 3: User Connects with Another Institution (FI2)
- If the user wants to use services from another financial institution (FI2), they don’t need to submit the same documents again.
Instead:
- The user gives FI2 permission to check the verification done by FI1 through the blockchain.
- FI2 doesn’t see the actual documents but can trust FI1’s hash
It stops repeating KYC steps, lowers costs, and safeguards user privacy. As a result, the user stays in control of who can access their information.
Step 4: FI2 Checks the Hash to Confirm the Data
FI2 now verifies if the data is real:
- It gets the hash stored by FI1 from the blockchain
- It creates a new hash using the documents it received or got access to.
- It compares this new hash with the one on the blockchain.
- If they match, FI2 knows the data is accurate and verified and can onboard fast.
- If they don’t, it could mean the data changed or is outdated, so FI2 will check again.
This makes sure the identity is real and safe. It does this without showing the actual data by using blockchain to find any changes.
Step 5: Updating Documents and Keeping Records
KYC data can change with time. For example, you may get a new passport or, you may shift to a new address. Well, when this happens, you send the new documents to FI1. What happens then? FI1 simply reviews the data and verifies everything. Once done, it creates a new hash. This new hash is added to the blockchain.
Now, here’s what smart contracts can do:
- They can quickly tell FI2 or any other group that saw the data before.
- They can also keep a full list of all changes and who made them.
Because of this, your KYC data stays fresh and correct. It also follows the rules. And best of all, every action is saved, so things stay clear and fair.
What Are the Benefits Of Using Blockchain in the KYC Process?
Blockchain improves KYC. It adds safety and speed, and protects customer data. It also makes identity checks easier and faster.
Real-Time Data Sharing
When you update a user’s info in blockchain KYC, the change is updated instantly. This means all other systems get the new data quickly. Thus, the whole system always has the latest verified info. Because of this, users don’t need to send their documents again and again. That makes the process easier and faster for everyone.
Less Repetition and Faster Onboarding
In regular systems, users have to do KYC again at each new service. It’s frustrating and time-consuming. On the other hand, Once verified on the blockchain, users can share their data with approved platforms only if they choose to. This cuts down repeated checks, lessens paperwork, and helps new customers get started faster.
Smoother Customer Experience
With blockchain, KYC is done just once. The verified info is stored securely and shared with other platforms or institutions only when the user agrees. This avoids repeating the same steps and makes everything quicker and more comfortable.
Less Manual Work
With blockchain, essential KYC tasks like verification and data handling are handled automatically. So, staff don’t need to deal with physical documents or manual data entry. This lowers errors, speeds things up, reduces costs and makes the process smoother and more dependable.
Improved Data Quality
Whenever a user updates their KYC details, the system records the precise time of the change. This creates a transparent and dependable history of all modifications. Consequently, institutions have access to up-to-date and accurate data. Regulators can also monitor these updates easily, ensuring the information remains trustworthy for all parties.
What Are the Challenges of Blockchain Based KYC?
Using blockchain for KYC is promising, though it’s not without its problems. Technical limits, privacy concerns, and global variations make broad adoption tough. Understanding these challenges helps create better solutions.
- Setting up is hard and expensive for small businesses.
- It’s tough to connect with old systems.
- Countries differ in ID and privacy regulations
- You can’t easily change or delete data on the blockchain, which can cause privacy problems.
- Keeping sensitive data on the blockchain is risky and limited.
- Keeping data outside the blockchain can get messy.
New privacy options are around, but they’re still a bit rare in use. - Because there’s no global KYC rule, working together gets tricky.
- Public blockchains can slow down when many people use them.
- There can still be hacks or problems with the network.
- Managing access and private keys is risky.
- Updating user info on the blockchain is difficult.
- Outdated or incorrect data risks legal issues.
Blockchain KYC Use Cases
By applying blockchain to KYC, companies can fight fraud, streamline onboarding, and cut costs, all while protecting user privacy. The main use cases include:
| Use Case | How Blockchain Helps | How KYC Works with Blockchain | Example Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Services | Checks identity without a central control | Banks share verified customer info securely | Banks, lenders, and payment companies share IDs |
| Regulatory Compliance | Uses smart contracts and keeps unchangeable records | KYC and AML rules followed automatically with logs | Banks follow rules easily with automatic checks |
| Identity Management | Users control their own ID data | People decide what info to share and with whom | Digital ID platforms for safe user login |
| Cross-Border Payments | KYC info works across countries | One verified KYC is profile used by many institutions | Money transfers are verified quickly across borders |
| Insurance | Policyholder info can’t be changed | Instant ID checks linked to claims and policies | Insurance companies verify customers during claims |
| Real Estate Transactions | ID and documents stored safely on blockchain | Secure KYC connected to property sales | Real estate sites verify buyers and sellers |
| Cryptocurrency Exchanges | Shares KYC info without delay | Real-time ID checks when opening accounts or trading | Crypto exchanges speed up user signup and stop fraud |
| Healthcare | Protects privacy and controls consent | Patient ID checked while keeping data safe | Hospitals check patient IDs and consent securely |
The Future Trends in KYC and Identity Proofing
In 2025, Blockchain KYC is changing fast to handle new problems and chances. Stronger rules, especially in places like the EU, are making companies use safer ways to check people’s identities, like digital wallets and portable IDs. Many of these innovations are being powered by enterprise blockchain solutions, which offer secure, scalable, and permissioned systems designed for compliance.
While identity fraud methods improve, especially deepfakes, AI tools must evolve to detect them swiftly. Another big change is using perpetual KYC, which means checking customers all the time automatically, not just once in a while. These changes help make identity checks faster, safer, and easier while following the new rules.
To keep up with these trends, many organizations are partnering with the blockchain development companies that specialize in KYC and identity solutions.
Final Thoughts
KYC on blockchain is not just a trend; it offers a better way to handle identity checks by making the process faster and safer. Because of this, businesses can lower costs and smoother onboarding. At the same time, it’s a chance to build trust-first systems from day one for startups. And for compliance teams, it offers real-time verification, stronger data security, and easier audits.
Since this shift is already underway, adopting blockchain-based KYC early is the best way to stay ahead. For secure and scalable solutions, partner with the best blockchain development company and start building the future today.
FAQs
Can blockchain KYC replace traditional identity documents?
Not fully. Blockchain KYC can store and verify digital identities, but it still depends on real-world documents like passports or national IDs to start the process.
How does blockchain KYC comply with data protection laws like GDPR?
Blockchain KYC follows GDPR by keeping sensitive data off chain, using encryption or ZKPs to verify identity without exposing details and controlling access through permissioned systems. This helps protect user privacy while still meeting transparency rules.
How does blockchain KYC handle identity verification for unbanked or undocumented users?
Blockchain KYC can help unbanked or undocumented users by using decentralized IDs and verifiable credentials backed by alternative data and basic biometrics, but it still can’t replace official document.
How scalable are blockchain KYC systems for large user bases?
Blockchain KYC can scale pretty well especially with permissioned chains and Layer-2 tech, though public blockchains still struggle with lower TPS. Enterprise setups handle large user bases better.
How does blockchain KYC impact the cost structure for financial institutions?
Blockchain KYC cuts costs for financial institutions by reducing repeated checks, automating verification with smart contracts, and lowering manual work.
Can blockchain KYC integrate with existing legacy systems?
Yes, but it’s not always smooth. APIs and middleware can connect blockchain data with old banking systems though it takes effort and custom development.













